Advanced Analytics Techniques: Leveraging Google Analytics Secondary Dimension
Wiki Article
Opening the Power of Secondary Measurement Analytics for Enhanced Information Insights and Decision-Making
In the world of information analytics, main measurements commonly take the limelight, however the real depth of insights lies within the world of second measurements. By using the power of additional measurement analytics, organizations can unveil hidden trends, reveal relationships, and essence a lot more significant final thoughts from their data.
Importance of Second Measurements
Checking out the importance of secondary measurements in analytics reveals the covert layers of data understandings vital for notified decision-making in various domains. Second dimensions offer a much deeper understanding of key information by providing additional context and viewpoints. By including additional measurements right into analytics, companies can draw out a lot more extensive and nuanced insights from their datasets.One trick significance of secondary measurements is their ability to sector and categorize main information, permitting for a more detailed evaluation of specific parts within a dataset. This segmentation makes it possible for services to identify patterns, fads, and outliers that might not be apparent when checking out the data in its entirety. Additionally, secondary dimensions aid in uncovering relationships and dependencies in between different variables, causing more precise projecting and anticipating modeling.
In addition, second dimensions play a vital duty in boosting data visualization and coverage. By including secondary dimensions to visualizations, such as charts or graphes, analysts can create a lot more informative and insightful depictions of information, promoting far better communication of findings to stakeholders. Overall, the integration of secondary dimensions in analytics contributes in unlocking the full capacity of data and driving evidence-based decision-making.
Secret Benefits of Using Additional Dimensions
Utilizing secondary dimensions in analytics offers organizations a strategic advantage by augmenting the deepness and granularity of information understandings. One crucial benefit of integrating secondary dimensions is the capacity to segment and filter information, enabling an extra in-depth evaluation of particular aspects within a dataset. This segmentation makes it possible for companies to get a much more nuanced understanding of their audience, performance metrics, and various other crucial information factors. By exploring data using second measurements such as time, place, device type, or customer demographics, companies can discover patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise continue to be concealed.Furthermore, the usage of secondary measurements boosts the context in which main data is translated. It provides an extra detailed view of the partnerships in between various variables, allowing companies to make educated choices based on a much more holistic understanding of their information. Additionally, additional dimensions promote the identification of outliers, abnormalities, and areas for optimization, inevitably resulting in more reliable techniques and boosted outcomes. By leveraging additional dimensions in analytics, organizations can harness the complete possibility of their data to drive much better decision-making and accomplish their business goals.
Advanced Data Analysis Methods
A deep study advanced data analysis methods exposes innovative approaches for drawing out beneficial insights from complex datasets. One such strategy is artificial intelligence, where formulas are employed to identify patterns within data, forecast results, and make data-driven choices. This approach permits for the automation of logical design structure, allowing the processing of big volumes of data at a faster pace than traditional approaches.An additional innovative strategy is anticipating analytics, which utilizes statistical formulas and equipment understanding strategies to forecast future outcomes based on historic information. By evaluating trends and patterns, organizations can prepare for consumer habits, market patterns, and potential threats, encouraging them to make positive decisions.
In addition, message mining and sentiment evaluation are useful methods for extracting understandings from unstructured data resources such as social networks comments, consumer evaluations, and survey feedbacks. By examining text information, organizations can recognize client opinions, recognize emerging fads, and improve their product and services based on comments.
Enhancing Decision-Making With Second Dimensions
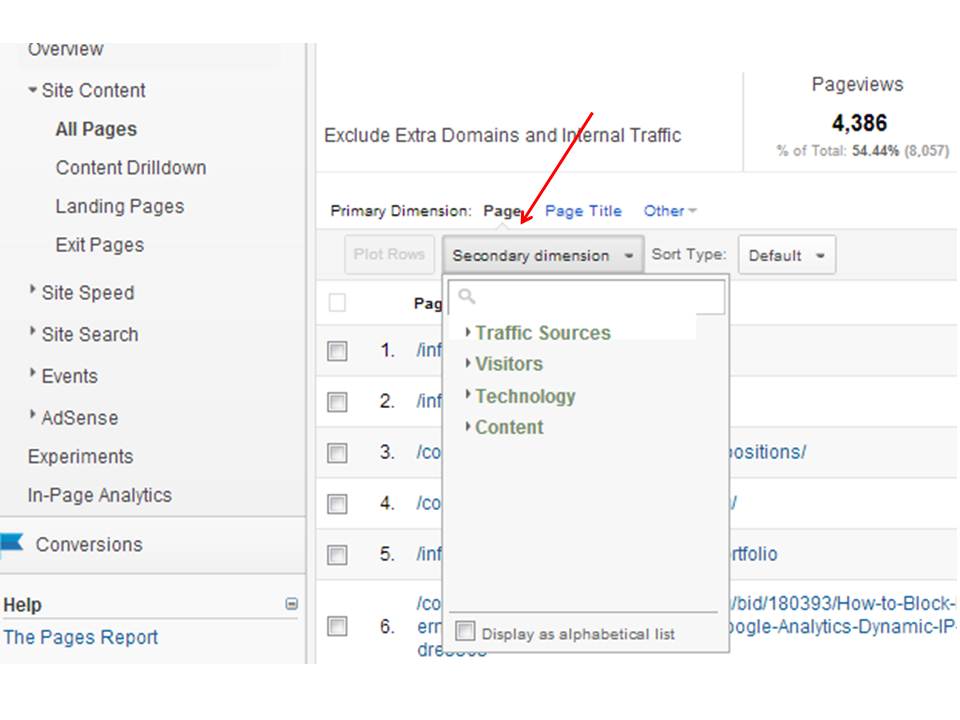
Enhancing decision-making through second dimensions allows organizations to make more notified and targeted strategic choices. By segmenting consumer information based on secondary dimensions like purchasing history or involvement levels, business can customize their advertising and marketing strategies to particular audience sectors, leading to improved conversion rates and best site consumer contentment. Secondary dimensions can help recognize relationships and partnerships in between various variables, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions that drive growth and profitability.
Implementing Secondary Measurement Analytics
When integrating second measurements in analytics, organizations can open deeper understandings that drive tactical decision-making and boost general efficiency. This involves understanding the certain questions the company seeks to respond to and the data factors required to resolve them.
Furthermore, companies need to take advantage of progressed analytics tools and innovations to simplify the process of integrating second dimensions. These tools can automate information processing, analysis, and visualization, enabling companies to focus on translating understandings instead than manual data adjustment.
Verdict
In conclusion, secondary measurement analytics play a crucial role in enhancing information understandings and decision-making procedures. By using sophisticated data Home Page analysis techniques and implementing secondary measurements properly, companies can open the power of their data to drive tactical company decisions.In the world of information analytics, main dimensions frequently take the spotlight, yet the real depth continue reading this of insights exists within the world of additional dimensions.Utilizing second measurements in analytics provides organizations a strategic benefit by increasing the depth and granularity of information understandings. By leveraging secondary measurements in analytics, companies can harness the full possibility of their information to drive better decision-making and attain their service goals.
Implementing information validation procedures and routine audits can help keep data top quality and dependability.
By utilizing innovative data evaluation methods and implementing additional dimensions properly, organizations can open the power of their data to drive critical service decisions.
Report this wiki page